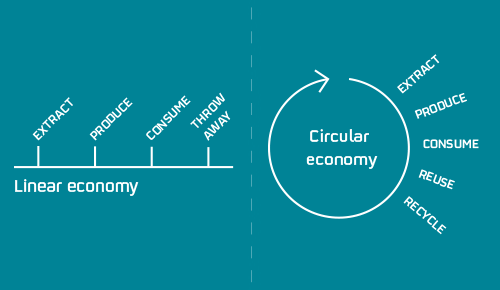
What are the benefits of the circular economy?
What are the benefits of the circular economy?
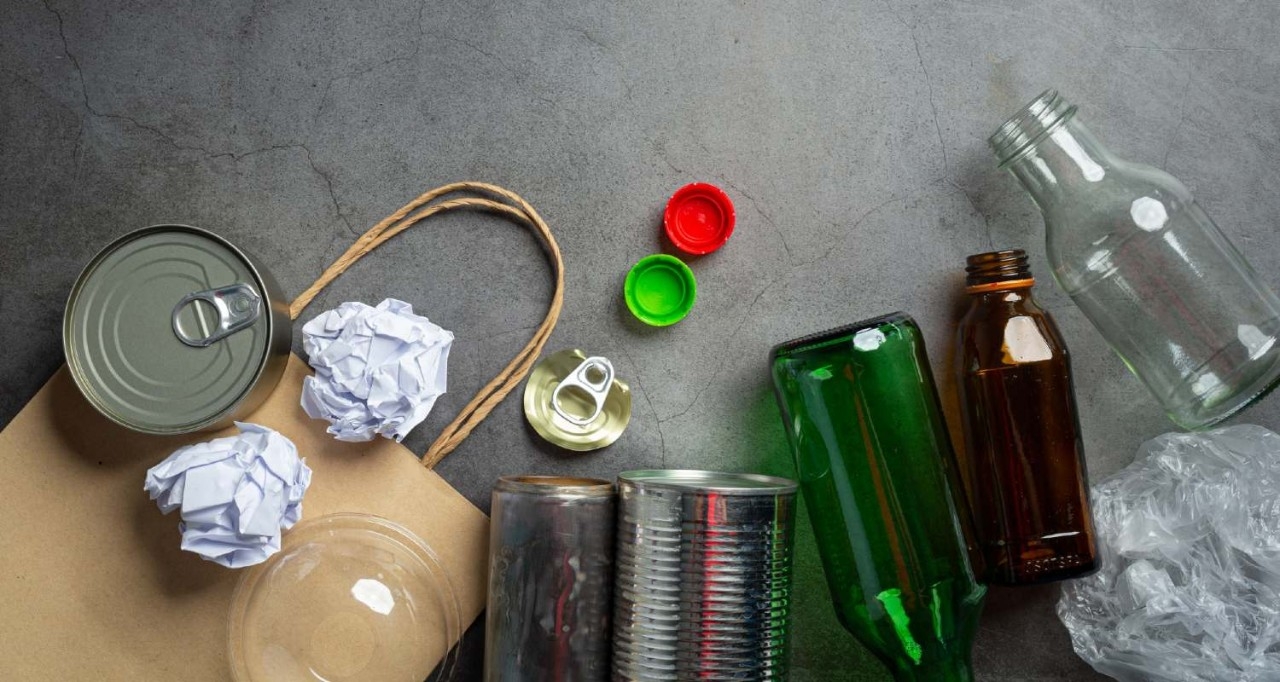
Protects the environment
Protects the environment
It reduces emissions, minimises the consumption of natural resources and reduces waste generation.
Benefits the local economy
Benefits the local economy
It can benefit the local economy by encouraging production models based on the reuse of nearby waste as raw material.
Drives employment growth
Drives employment growth
It stimulates the development of a new, more innovative and competitive industrial model, higher economic growth, and more employment.
Promotes resource independence
Promotes resource independence
The reuse of local resources can lead to less dependence on imported raw materials.