
All about the Internet of Things
All about the Internet of Things
Technology. Innovation. Quality of life
Technology. Innovation. Quality of life
Technology is revolutionizing our way of interacting with the world, while offering us more comfort and quality of life: There are already coffee makers that prepare our coffee automatically when our alarm goes off, while the car offers us indications in real time to avoid traffic jams. All of this and much more is today a reality thanks to the Internet of Things (IOT).
What is the Internet of Things?
What is the Internet of Things?
The Internet of Things refers to the connection of everyday objects to the Internet so that they can communicate with each other and with us.
These objects have special sensors that allow them to collect data and send it through the internet. This way, we can control devices and interact with them from anywhere through our phone or computer.
The Internet of Things isn't only used in household devices or vehicles, it's also applied in areas such as health, agriculture, and industry, amongst others.
How does the Internet of Things work?
How does the Internet of Things work?
The IoT is based on systems that monitor, adjust, and collect the interactions between the various connected devices. For example, if we have a smart thermostat at home, and it detects that the temperature is very low or very high, it sends the information through the internet to a server. The server processes the data, and from it, it can send automatic instructions (such as connecting the air conditioning if it is too warm) or send you phone notifications to let you know what is happening to let you decide.
Therefore, in addition to the connected objects themselves, the Internet of Things relies on sensors, internet access, servers, and data processing systems so that information can be sent and received.
Work at Repsol
We’re looking for talented people who can help us create value sustainably. Find opportunities that you can take advantage of to continue growing.
Advantages of the Internet of Things at home
Advantages of the Internet of Things at home
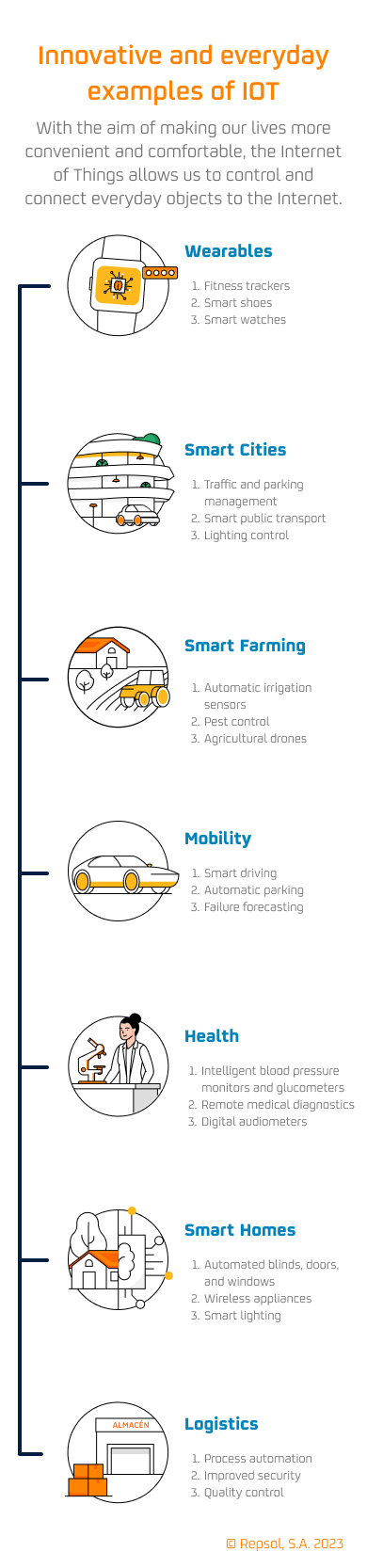
Examples of everyday Internet of Things
Examples of everyday Internet of Things
- We have devices (such as smart watches or fitness trackers) that can record data such as heart rate, sleep quality, and physical activity to control health status and sports level, amongst others. There are also blood pressure monitors and glucometers capable of sending data to a physician in real time or making decisions such as administering a dose of insulin by means of a pump if the patient needs it.
- In the urban environment, smart cities apply IoT to connect and manage aspects such as energy, waste management, transportation, and security. For example, it's possible to optimize the on/off schedule of streetlights to minimize energy consumption, or to detect traffic jams and allow the opening of alternative routes to mitigate their impact.
- Smart grids make the most of the IoT potential to improve their performance and efficiency: They can detect faults, optimize the management of renewable energies, and control infrastructure. Furthermore, smart meters allow consumers to make adjustments in real time, while helping companies to optimize energy distribution.
- In the field of logistics, the IoT is used in the so-called connected logistics, which links the various elements of the supply chain. For instance, sensors and IoT devices are used to track where products are in each moment, as well as to improve the distribution of loads and find out the status of vehicles. This allows for fine-tuning of planning, tracking, and deliveries.
- The same happens with digital supply chains, which collect data in real time on production, storage, and transportation of products, which results in better planning, inventory optimization, tracking, and traceability.
Advantages of the Internet of Things in industry 4.0
Advantages of the Internet of Things in industry 4.0
In the IoT, the following aspects stand out:
- Data collection: Numerous parameters (temperature, humidity, pressure, energy consumption, etc.) can be monitored through sensors and devices in order to collect information on the performance and status of industry processes and assets thanks to artificial intelligence.
- Connectivity: Just like with the conventional IoT, connectivity allows data to be transmitted to systems and databases for analysis.
- Data analysis: Through techniques, such as machine learning or big data, errors and faults can be detected, production can be optimized, and we can determine the performance of systems, such as with machine learning tools.
- Automation: This data allows measures to be taken in real time and adjustments to be made to prevent faults, as well as improve energy efficiency and production performance.
- Security: It's essential to implement measures, such as data encryption or network segmentation, to ensure the data confidentiality and protect industrial systems.
The IIoT is making significant progress in the development of industrial processes, while it enables methodologies to be optimized and innovations to be introduced in this field, such as disruptive technologies.

Repsol and the Internet of Things in the energy sector
Repsol and the Internet of Things in the energy sector
At Repsol, we are also promoting this technology through our IoT platform, which allows us to manage and capture data from different devices in real time. We thus manage to cut development times, promote effective collaboration between operations, improve our solutions, and enable their ongoing evolution. These are some of the applications that are already in operation:
- Service stations. At our service stations, we have implemented the ElIoT initiative, which uses a series of IoT sensors to monitor elements related to the car wash, the store, and the track. In this way, we can find out, for example, habits and optimize the energy efficiency of our stations.
- Telemetry. Moreover, in our LPG business (mixture of butane and propane gas), we have launched the Telemetry project, which, through sensors in the bulk tanks, helps us to monitor our customers' consumption and replenish the product when necessary.
- Repsol Technology Lab projects. In addition, at our innovation and technology center, Repsol Technology Lab, we supervise, amongst other things, the performance and behavior of batteries in their management of energy loads. In the industrial field, the integration of the IoT Platform allows us to optimize the performance of our assets, among other matters.
Biotechnology
Biotechnology
Applications, types, and advantages of this science that seeks to improve people's lives.

What is home automation?
Do you want to know what advantages it has for your home?

