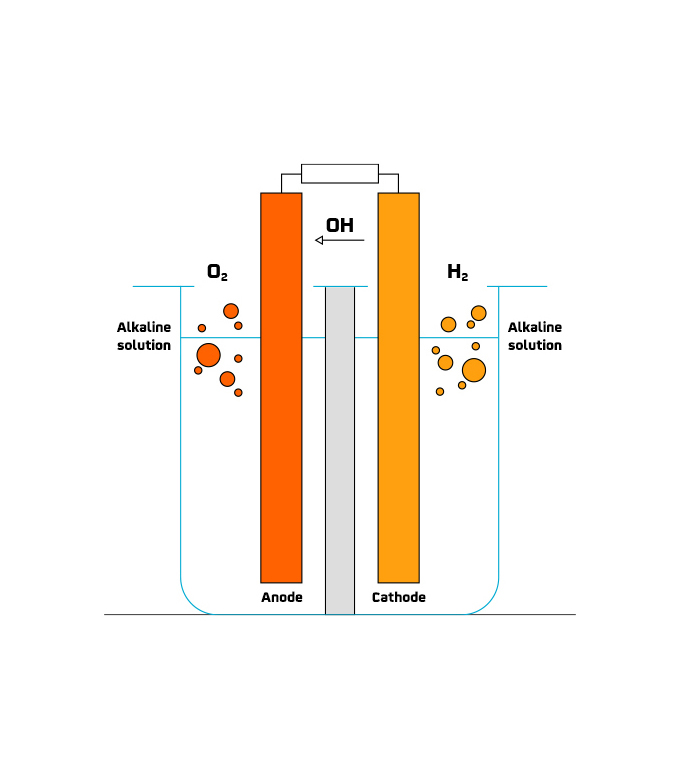
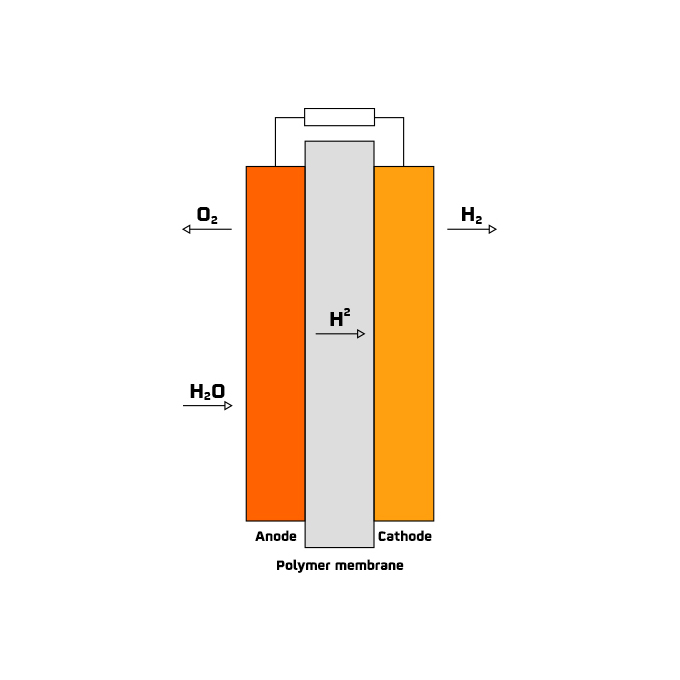
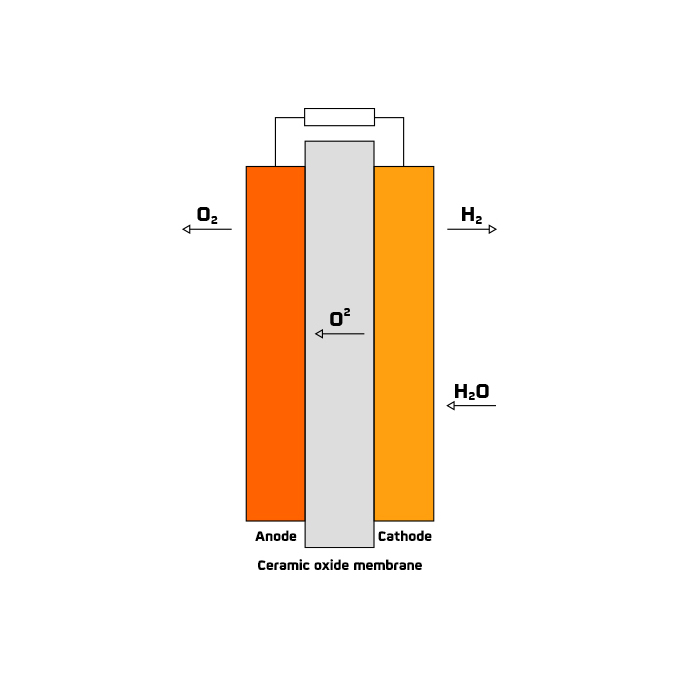
The commitment to renewable hydrogen generation is strong in several countries. In fact, the European Commission presented the document "A hydrogen strategy for a climate-neutral Europe" in mid-2020, and in 2022 the green light was given for the investment of 5.2 billion euros in public funding to promote hydrogen research and innovation.
At Repsol, we work alongside Petronor to promote renewable hydrogen on the Iberian Peninsula. For this reason, we are installing the first electrolyzer in the Basque Country, in Petronor's industrial complex in Muskiz. It will have a capacity of 2.5 MW and will entail an investment of 8.9 million euros.
The project will be integrated within the Basque Hydrogen Corridor (BH2C), an initiative that 80 entities have already signed up to and aims to boost economic recovery not only in the Basque Country, while making progress in the decarbonization of the energy sector. In Cartagena, it is also planned to activate an electrolyzer with a capacity of 100 MW, as part of the Green Hydrogen Initiative of the Region of Murcia, focused on the Escombreras Valley area.
However, the most ambitious project so far by Repsol will be implemented in Tarragona. It is an electrolyzer with a capacity of 150 MW by 2026 and 1,000 from 2027. This facility will have the best technologies to minimize the consumption of water destined for renewable hydrogen production.