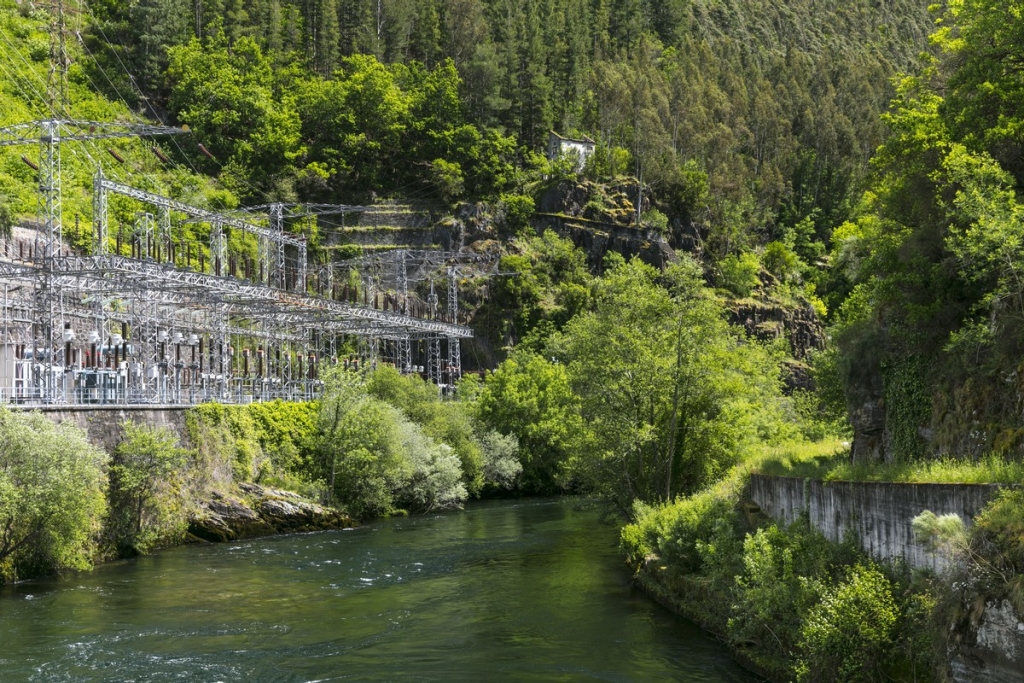
Run-of-river hydropower plants
Run-of-river hydropower plants
They harness the constant flow of water from rivers or streams, without using reservoirs. The water is diverted through a channel and directed through a pipe to a turbine that generates electricity. They are especially efficient and suitable for areas with constant flows of water.
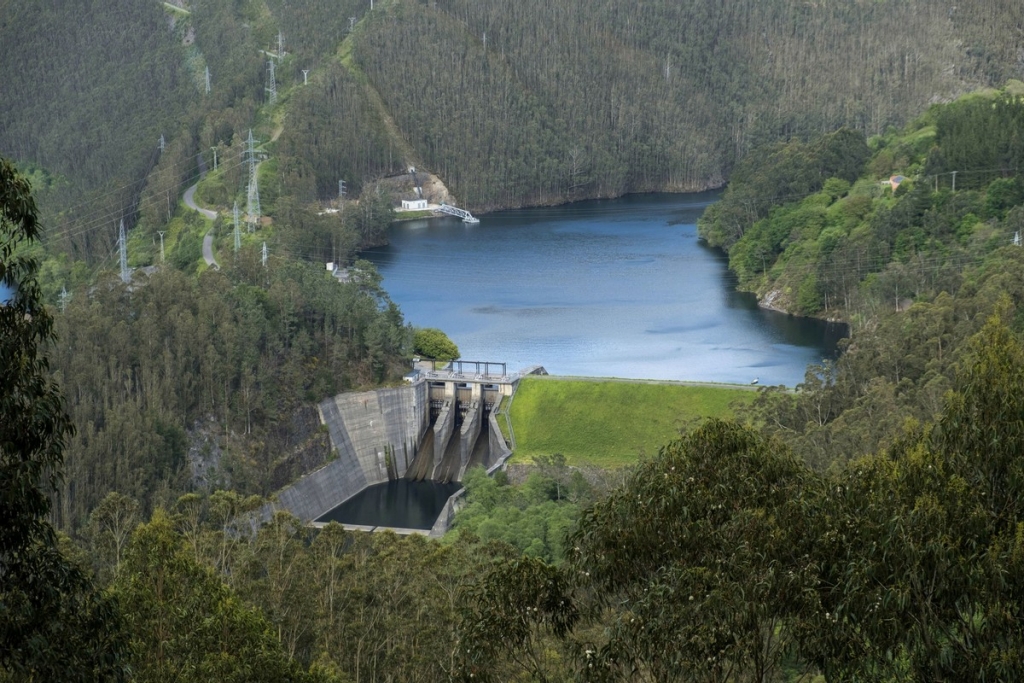

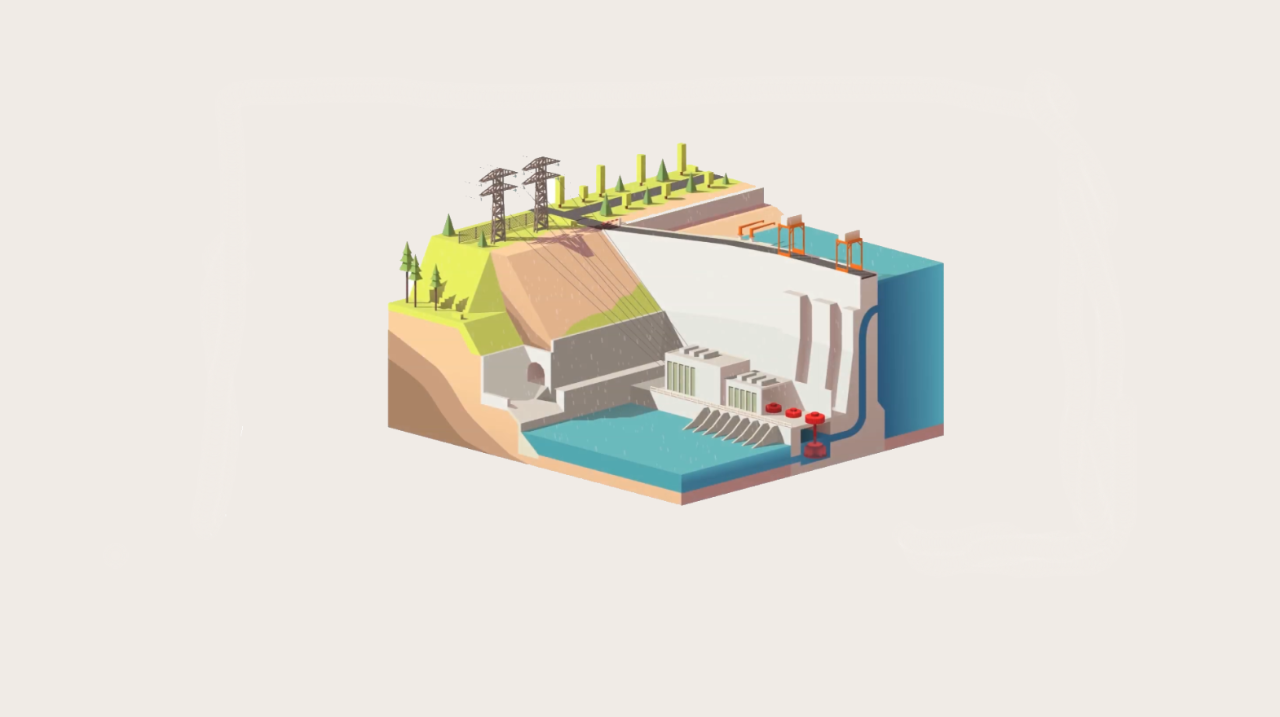
Hydropower plants with a reservoir
Hydropower plants with a reservoir
Water is stored in reservoirs and the flow to the turbines is regulated. They can be large scale (traditional hydropower plants), or smaller in size. Reservoirs offer flexibility to adjust electricity production according to demand.
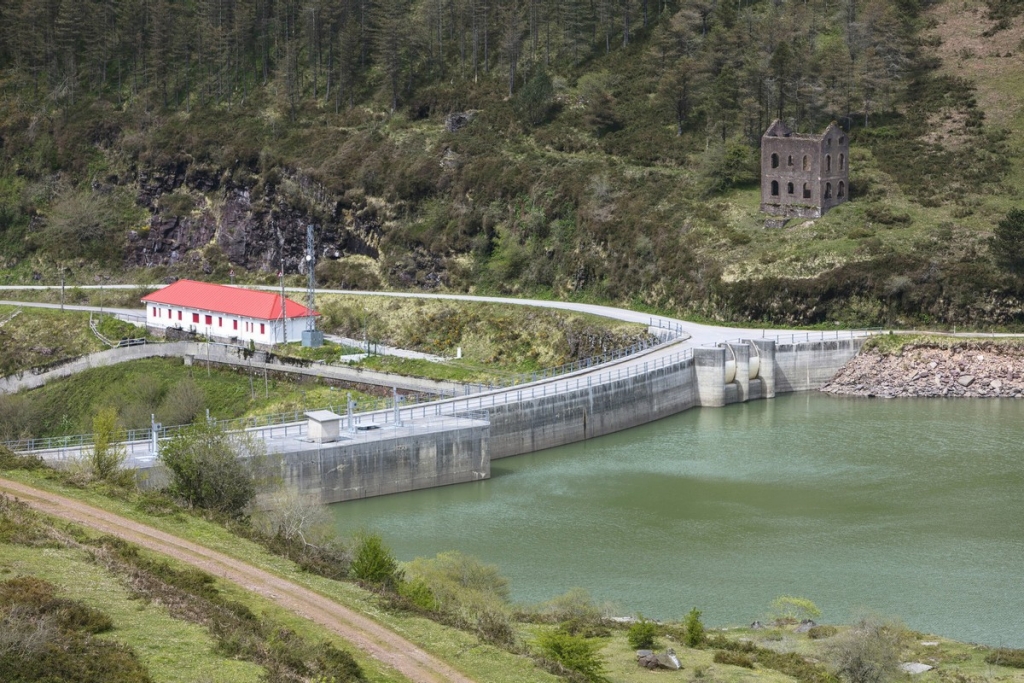

Pumped-storage hydropower plants
Pumped-storage hydropower plants
They are essential for storing energy. In periods of low demand they pump water from a lower reservoir to an upper reservoir using electricity. If it is high, water is released from the upper reservoir by hydraulic turbines. An example is the pumped-storage hydropower plant in Aguayo, Cantabria.
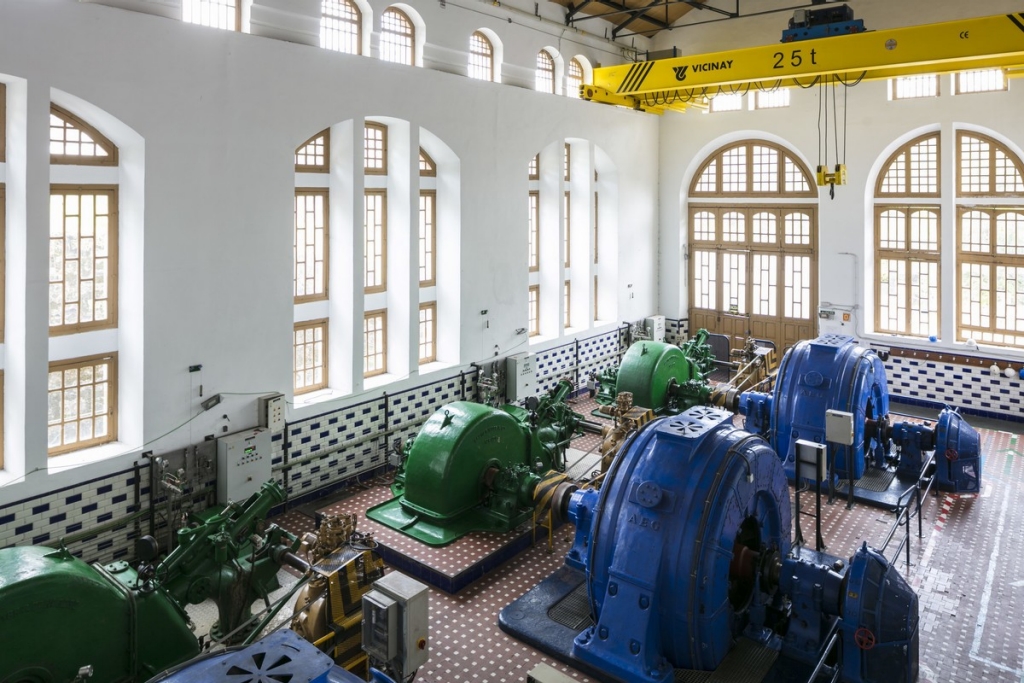

Bypass or channel hydropower plants
Bypass or channel hydropower plants
Instead of blocking the river with a dam, these plants divert part of the water flow through a channel to the turbines, allowing the river to continue its course. This minimizes environmental impact, although it reduces water storage capacity.
-scr.jpg)

-scr.jpg)


